Pregnancy and Prenatal Testing
Pregnancy is a remarkable and transformative period in a person’s life, marked by the development and nurturing of a new life within the womb. It is a time filled with anticipation, joy, and numerous physical and emotional changes. Throughout this journey, prenatal care and testing play a crucial role in ensuring the health and well-being of both the pregnant person and the developing fetus.
One significant aspect of prenatal care is prenatal testing, which involves various procedures and examinations to assess the health and development of the fetus and identify any potential risks or abnormalities.
Stages of pregnancy
The journey of pregnancy is typically divided into three main stages, known as trimesters. Each trimester represents a distinct phase of development for both the pregnant person and the growing fetus.
- First Trimester (Week 1 to Week 12):
- Second Trimester (Week 13 to Week 27):
- Third Trimester (Week 28 to Birth):
Prenatal Testing
Prenatal testing refers to a variety of medical procedures and tests conducted during pregnancy to assess the health and well-being of the fetus. These tests provide valuable information about the baby’s development, identify potential genetic or chromosomal abnormalities, and assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions regarding prenatal care and management.
Here are some common types of prenatal testing:
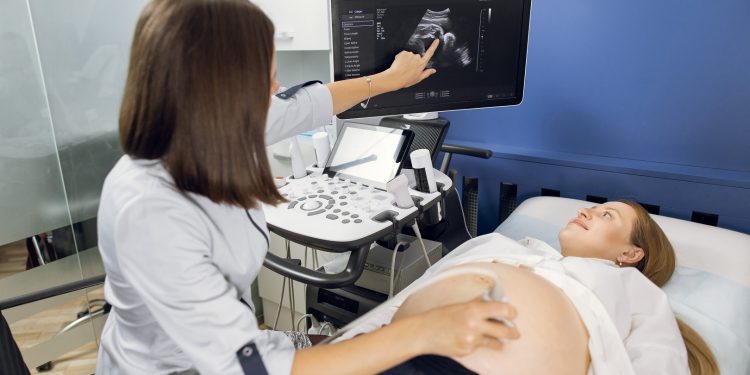
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging is a widely used and non-invasive test that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to create images of the developing fetus. It provides valuable information about the baby’s growth, anatomy, and position in the uterus. Ultrasounds are typically performed at various stages of pregnancy, allowing healthcare providers to monitor the baby’s development and detect any potential abnormalities.
- Maternal Blood Tests: Blood tests during pregnancy can provide important information about the health of the fetus. These tests measure various substances in the mother’s blood, such as hormones or proteins, that can indicate the risk of certain conditions. For example, maternal blood tests can screen for chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome (e.g., the triple or quadruple test) or neural tube defects (e.g., the alpha-fetoprotein test).
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT): NIPT is a newer and highly accurate screening test that analyzes fragments of fetal DNA in the mother’s blood. It screens for common chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (trisomy 13). NIPT is typically recommended for individuals at higher risk based on factors such as advanced maternal age or positive screening results from other tests. It poses no risk to the fetus as it only requires a maternal blood sample.
- Genetic Screening: Genetic screening tests are used to assess the risk of inherited genetic disorders or conditions. These tests may involve analyzing the genetic material of the fetus (e.g., amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling) or examining the parents’ genetic makeup and family history (e.g., carrier screening). Genetic screening is often recommended for individuals with a known family history of genetic disorders or specific ethnic backgrounds with increased risk.
- Diagnostic Tests: In cases where a higher level of certainty is required or when a specific condition is suspected, diagnostic tests can be performed. Examples include amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS). These tests involve the collection of fetal cells or tissue samples for genetic analysis. While they provide more definitive results, they are invasive procedures that carry a small risk of complications.
Purpose and Benefit of Prenatal Testing
- Detection of Genetic and Chromosomal Abnormalities: Prenatal testing allows for the identification of genetic disorders and chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. Tests like amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling (CVS), and non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) can screen for conditions such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, and others. Detecting these conditions before birth helps parents and healthcare providers make informed decisions regarding the management of the pregnancy, delivery plans, and potential medical interventions or treatments after birth.
- Early Intervention and Treatment: Prenatal testing can enable early intervention and treatment if certain conditions or abnormalities are detected. It allows healthcare providers to closely monitor the pregnancy, develop appropriate care plans, and provide specialized medical support when necessary. Early detection can lead to better management of certain conditions, such as initiating treatments or interventions shortly after birth, ensuring a smoother transition for the baby and providing a higher quality of life.
- Emotional Preparation and Decision-Making: Prenatal testing provides valuable information that can help expectant parents emotionally prepare for the birth of their child and make informed decisions about the pregnancy. Knowing about any potential genetic or chromosomal abnormalities allows parents to educate themselves about the condition, seek support, connect with specialized healthcare professionals, and plan for the unique needs of their child. This knowledge can help parents develop coping strategies, explore available resources, and make decisions about their future.
- Reducing Anxiety and Uncertainty: For individuals at higher risk or with specific concerns, prenatal testing can help alleviate anxiety and uncertainty during pregnancy. Knowing the results of tests can provide reassurance if the baby is determined to be healthy and free from specific genetic conditions. Conversely, if a condition is detected, it can help parents seek appropriate support, resources, and medical care, minimizing the unknowns and allowing them to proactively plan for their child’s needs.
- Facilitating Informed Decision-Making: Prenatal testing provides expectant parents with important information that enables them to make informed decisions about their pregnancy. Understanding the potential risks, challenges, and implications of certain conditions can help parents decide on the best course of action, whether it involves seeking additional medical consultations, opting for specialized care, or making decisions about the pregnancy itself. Prenatal testing empowers parents to be active participants in their healthcare journey, making choices that align with their values, beliefs, and individual circumstances.
Conclusion
Prenatal testing plays a crucial role in assessing the health and well-being of the fetus during pregnancy. These tests provide valuable information about the baby’s development, genetic or chromosomal abnormalities, and overall fetal health. The benefits of prenatal testing include early detection of potential conditions or abnormalities, facilitating early intervention and treatment, reducing anxiety and uncertainty for expectant parents, enabling emotional preparation and informed decision-making, and empowering individuals to actively participate in their healthcare journey.










Discussion about this post